
What does a stop sign mean?
A STOP sign is a regulatory road sign and traffic control device designed to inform drivers that they must come to a complete halt at an intersection or crossing and yield the right-of-way to other vehicles and pedestrians before proceeding.
Its purpose is to ensure road safety by preventing collisions and efficiently managing traffic flow.
With its distinct octagonal shape and bright red color, the stop sign plays a crucial role in road safety, making it a fundamental component of traffic control systems worldwide.
In this guide, we will explore the laws governing stop signs in the United States and various countries around the world and cover essential details such as regulations, size, shape, colors, and allowed materials for stop signs.
Join us as we embark on this international journey through the world of stop signs.
Stop Signs
Let’s first take a brief detour by traveling back in time more than 100 years ago to Detroit, Michigan, to understand the origins of the now ubiquitous stop sign and regulatory traffic device.
Who Invented the Stop Sign?
The origin of stop signs dates back to the early 20th century, specifically in 1914, when the first known stop sign was created by Detroit police sergeant Harold “Harry” Jackson to simplify his job managing traffic at an intersection with low visibility.
He fashioned it out of a piece of plywood that he cut the corners off of and inscribed “STOP” at the center. He saw how its intuitive function helped regulate traffic flow, and in the following years, stop signs began to be adopted across cities in Michigan, America, and the rest of the world.

The modern-day red and octagonal stop sign was standardized in the United States in 1954 by the American Association of State Highway Officials (AASHO) to improve visibility and recognition.
The octagonal shape, which had been in use since 1922, was chosen to distinguish the stop sign from other traffic signs, ensuring it was easily recognizable even at night or when the sign was partially obscured.
Today, following numerous stop sign-controlled intersection case studies and adoption, the red octagon, meaning stop, is an internationally recognized traffic control device, serving as a critical component of road safety measures worldwide.
Fast Fact: Stop Sign even received its own official emoji 🛑 (Octagonal Sign emoji) in 2016.
Now, let’s shift our focus to the required standards and design features of stop signs.
Standard Stop Sign Design Specifications
The following are the standard design characteristics of stop signs in the United States and most of the world:
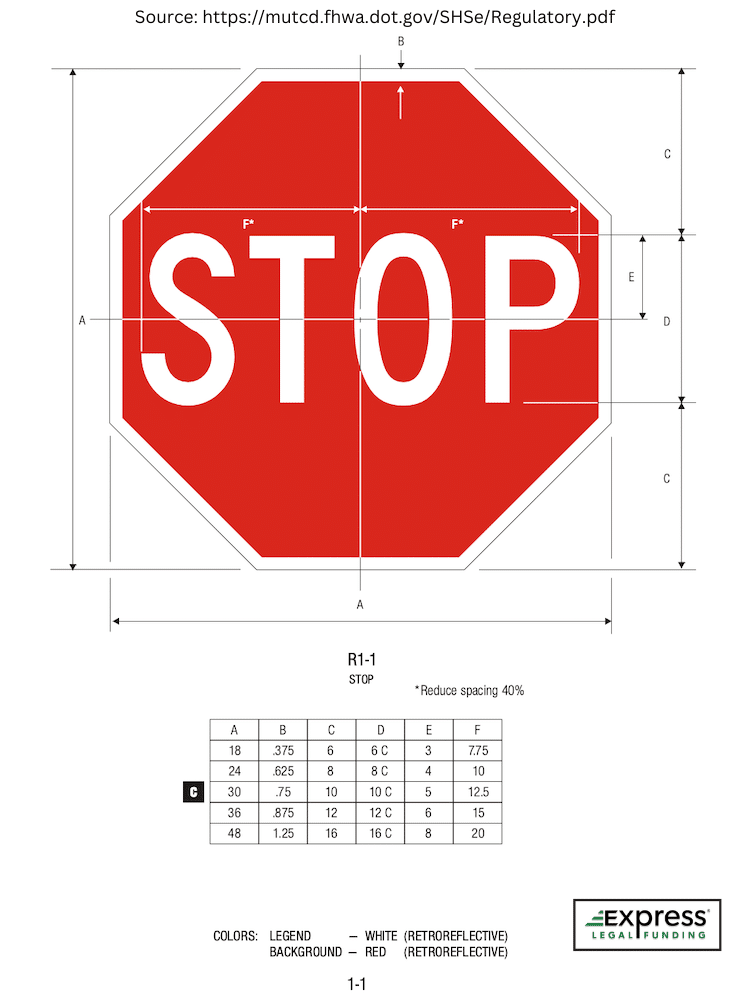
What is the shape of a stop sign?
Stop Sign Shape
A stop sign is an equilateral octagon (8 sides with the same length) that is flat in shape, which is a unique shape among regulatory road signs, helping drivers recognize the sign from a distance, even when the front of the sign is not visible.
Stop Sign Color
The background color of a stop sign is red, which, like flashing red lights, is universally recognized as a color denoting prohibition and danger. The border and the text on stop signs are white, creating a high contrast for easy visibility.
Stop Sign Lettering
The word “STOP” is displayed in white bold capital letters.
What font do stop signs use?
Stop Sign Font Name Is Highway Gothic
The font “Highway Gothic,” developed by the Federal Highway Administration, is a sans-serif font designed to be clear and legible. It is intended to be easily read from a distance by drivers approaching the signage.

What are the dimensions of a stop sign?
Stop Sign Dimensions
The size of stop signs can vary depending on the location and the specific regulations of a country or region. However, in many countries, including the United States, 30 inches is the minimum size required for stop signs.
- For rural areas and single-lane roads, the standard stop sign size is 30 inches (75 cm) across from one flat side to the opposite flat side.
- In some urban areas (not in the U.S.), a smaller size may be used, often 24 inches (60 cm) across.
- On multi-lane or high-speed roads, larger sizes, such as 36 inches (90 cm) across, may be required to ensure visibility.
These design characteristics are standardized to ensure that stop signs are easily recognizable and uniformly understood by drivers, regardless of the country they are driving in.
This standardization is critical in road safety by helping prevent accidents and efficiently manage traffic flow.
Stop signs are used worldwide to inform drivers that they must come to a complete stop at an intersection or road junction. While typically similar, the design and implementation of stop signs can vary from one country to another.
Below are some of the variations in stop signs across different countries, including a brief recap of the previously discussed design details in the United States for uniformity and context:
Stop Signs in the United States

- Shape, Color, and Words: The stop sign in the U.S. is a red octagon with a white border and the word “STOP” printed in uppercase white letters on a red background.
- Size: The standard stop sign dimensions in urban areas are at least 30 inches (76 cm) across opposite flats of the octagon with a 3/4-inch (2 cm) white border in the United States. The “STOP,” printed in all caps in the center of the sign, must be 10 inches (25 cm) tall.
- Mounting Height: The height of the stop sign installation from the bottom edge to the road level should be 5 feet in rural areas. In business, commercial, or residential areas where parking is allowed on the side of the road, stop signs must be installed 7 feet above the ground.
- Stop Sign Placement: Stop signs are placed on the right side of roadways 6 feet from the pavement edge (12 feet minimum in rural areas if there is no shoulder keeping drivers off the side of the road) and even with the stop line or 4 feet in front of a crosswalk.
- Retroreflectivity or Illumination: Stop signs must be retroreflective (reflect headlights back) or illuminated (light behind sign face or LEDs) to show the same shape and similar road sign color by both day and night. There are additional criteria about the type and placement of the “shiny” materials and minimal measure of retroreflectivity.
- Supplemental Plaques: In some cases, supplementary plaques may be used with stop signs to convey additional information, such as “ALL WAY” to indicate an all-way stop at an intersection, or “4-WAY” or “3-WAY”, and instructions like “STOP HERE ON RED.”
- Regulations: In the United States, regulations and guidance for stop signs are detailed in the Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD), which standardizes their location, height, and distance from intersections.
Learn more about these stop sign rules below:
Regulatory Standards For Stop Signs in the United States
In the United States, stop sign regulatory standards, including design, placement, and usage, are primarily governed by the Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD), which was recently updated in December 2023. Download a free copy of the MUTCD 11th Edition.

The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) publishes the MUTCD to set the guidelines for all traffic control devices and pavement markings on public roads and highways (interstate and intrastate) to ensure these critical traffic control devices are uniform, visible, and understandable across all jurisdictions.
Compliance with the MUTCD is essential for achieving and enhancing road safety by facilitating smooth traffic flow for drivers, cyclists, and pedestrians across the country.
Compliance and Regional Road Sign Variations
While the MUTCD sets the federal guidelines, states and local jurisdictions can have additional regulations or slight variations as long as they do not conflict with the national standards.
At the state and local levels, road and transportation authorities must ensure that all traffic control devices, including stop signs, comply with the MUTCD to promote uniformity and avoid confusion among road users.
MUTCD Updates and Revisions
The FHWA periodically updates the MUTCD to adjust for insights from new research, technology, and practices in traffic control and road safety.

As such, engineers and local authorities must stay on top of any changes to ensure that their traffic control devices remain compliant with the latest standards, especially when beginning new construction projects.
Stop Signs in the European Union
- Shape and Color: In the European Union (E.U.), STOP signs are generally octagonal with white lettering on a red background, similar to the U.S.
- Wording and Language: The word “STOP” is used, which is universally recognized across E.U. countries, even though local languages may have different words meaning stop.
- Regulations: In the E.U., traffic signs, including stop signs, are standardized widely across member countries through various directives and agreements, with the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals being the primary factor. More details below:
Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals (1968)
Although not a European-specific document, this international treaty from the United Nations has been adopted by almost all countries in Europe (Andorra, Ireland, Iceland, Malta, and Monaco are the only European countries that are not parties to the convention).
Directive 2008/96/EC on Road Infrastructure Safety Management
This European Parliament directive aims to reduce road deaths and serious injuries on E.U. roads through safety assessments and audits. It mentions the importance of road signage for safety but does not specify particular design types.
Characteristics of Stop Signs in European Countries
Consistent with the Vienna Convention of Road Signs and Signals and its European Annex, stop signs are categorized as “B” priority signs and can be one of two types, with a few specific minor variants being accepted under the treaty and annex.
Traditional Red Octagon and Yellow Stop Sign

- Shape and Color: Octagon. White or light yellow border and a red background.
- Wording: The “STOP” legend is displayed in white or yellow letters, which may be written in English or the country’s national language.
- Size and Placement: While the general design is standardized, the size and placement of stop signs can vary slightly by country, adhering to national regulations and considering local road conditions.
Circular Stop Signs with Red Inverted Triangle
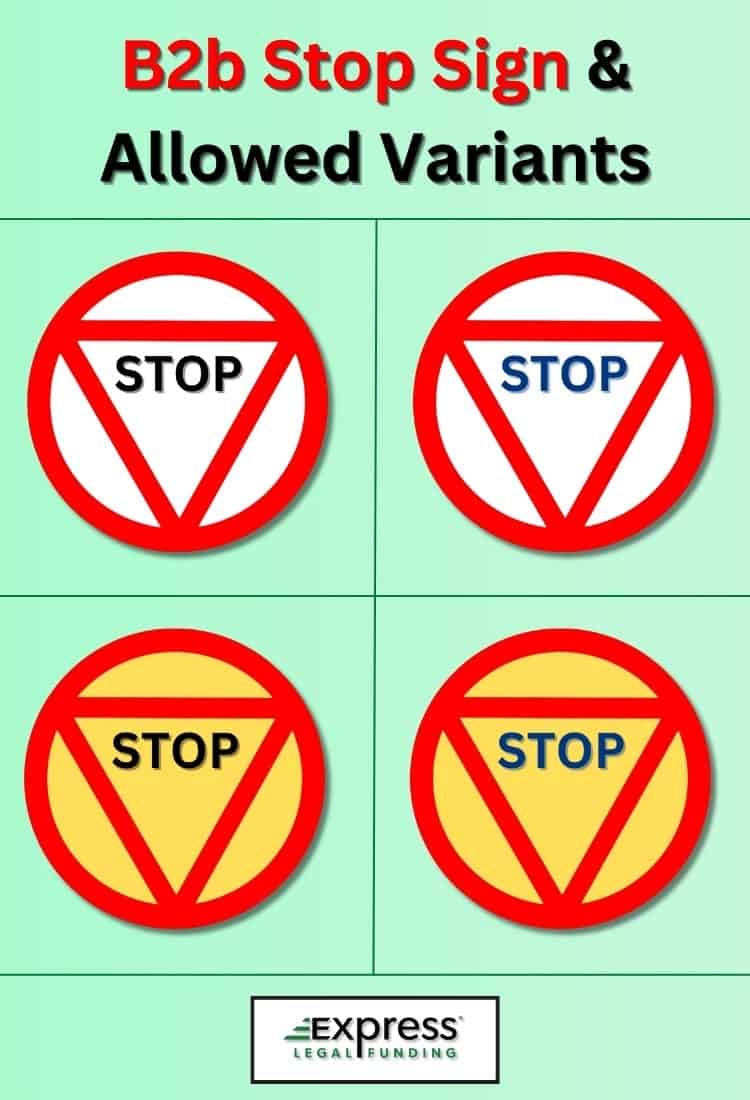
- Shape and Color: Circular. A red circle with a red inverted triangle with either a white or yellow background.
- Wording: The word “STOP” is displayed in black or dark blue letters, which may be written in English or the country’s national language.
- Size and Placement: While the general design is standardized, the size and placement of stop signs can vary slightly by country, adhering to national regulations and considering local road conditions.
E.U. Member Standardization Efforts
The E.U. continuously works towards further harmonizing road safety measures, including signage, through directives and the exchange of best practices among member states.
The European Commission’s Directorate-General for Mobility and Transport (DG MOVE) plays a crucial role in these efforts.
While there is a significant level of standardization for stop signs across the European Union, some variations exist due to language differences and national regulations.
The overarching goal is to ensure that regardless of these minor differences, the stop sign is universally recognizable to all drivers, contributing to road safety throughout the E.U.
Stop Signs in the United Kingdom

- Shape, Color, and Wording: Stop signs in the United Kingdom (U.K.) are red octagons with a white border and “STOP” written in white on a red background. Even Wales (Welsh), with its bilingual road signs, only has “STOP” on its stop signs.
- Size: The size of stop signs in the U.K. are required to be 75 cm (29.52″), 90 cm (35.43″), or 120 cm (47.24″), depending on the average speed of private cars traveling at the location (faster speeds requiring a taller sign height).
- Placement and Positioning: Stop signs must be placed at locations where drivers are required to come to a complete stop before proceeding. This is typically at minor road junctions where visibility is restricted or where traffic conditions make it necessary. The exact placement and stop signs in the U.K. factor in speed and visibility distance.
- Illumination and Reflectivity: Stop signs must be made of reflective material in the U.K. to ensure they are clearly visible at night or in poor weather conditions.
- Regulations: The design requirements and placement regulations for stop signs, as well as all other road signs and pavement markings, are governed by the Department for Transport in the U.K. These specifications are outlined in the Traffic Signs Regulations and General Directions 2016 (TSRGD).
Stop Signs in Japan

- Shape and Color: A stop sign in Japan is a red downward-pointing triangle with a white border.
- Wording and Language: Since 2017, the stop sign characters have been in Japanese and English. The word 止まれ (tomare), meaning “stop” in Japanese, is printed directly above “STOP.”
- Regulations: In Japan, the design of stop signs is regulated by the National Police Agency, which sets road signage standards per the Road Traffic Act.
Stop Signs in Brazil

- Shape, Color, and Wording: Brazil’s stop signs are similar to the standard design, with a red background and white lettering on an octagon. However, the word “PARE” is used, which means “STOP” in Portuguese (official and national language of Brazil).
- Regulations: Road signs in Brazil, like in many other South American countries, are firmly based on the US MUTCD standard but with text in Portuguese.
Other Latin American countries with “PARE” signs: Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, Puerto Rico, Uruguay, and Venezuela
Stop Signs in Arab Countries

- Shape and Color: The stop sign in almost all of the 22 Arab states (Middle East and North Africa, i.e., Egypt, Iraq, or U.A.E) is the standard octagonal shape with a red background, white border and multilingual white text.
- Wording and Language: The stop sign characters include the word “STOP” in English written under its Arabic equivalent, “قف” (qf), to accommodate both drivers who can and cannot read Arabic.
- Regulations: While stop signs are standardized widely across Arab countries and primarily modeled after the British road sign system, they are regulated at a national level.
Stop Signs in Israel

- Shape, Color, and Wording: In Israel, stop signs are octagonal with a red background and white border, but instead of the word “STOP,” which is “עצור” (atsúr) in Hebrew, or “قف “(qf) in Arabic, the signs display a simple graphic of a raised white hand denoting stop.
- Regulations: The Ministry of Transport and Road Safety regulates stop signs in Israel. Here is the Ministry’s official Guide to Transportation in Israel.
Stop Signs in China

- Shape and Color: Stop signs in Mainland China maintain the standard octagonal shape with a red background, white wording, and a white border.
- Wording: STOP signs in China feature the word “停” (Tíng), meaning “stop,” in prominent white characters that take up the majority of the surface.
- Regulations: Even though China has not signed the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, road signs in China closely resemble those found in Europe, the U.S., and Japan. The specifications for stop signs are outlined in the Guobiao standard GB 5678.2-2022.
- Exceptions: The text on stop signs in Hong Kong and Macau, China’s special administrative regions, differs from those in the rest of the country.
Stop Signs in Hong Kong

Stop signs in Hong Kong, where the official languages are English and Chinese, use the standard octagonal red background with white lettering with a white border, but the word “STOP” is above “停” with both being smaller font sizes to fit.
Stop Signs in Macau

In Macau, where the official languages are Portuguese and Chinese, the stop signs are similar to those in Portugal, which, like the United States, has a white border and the word “STOP” printed in white letters on red octagon background.
Stop Signs in Australia

- Shape, Color, and Wording: Stop signs in Australia are octagonal in shape. The background color of stop signs is red, with the word “STOP” inscribed in white letters.
- Size: The size of the stop sign may vary depending on its location (urban or rural) and the speed limits of the area. However, they are generally made large enough to be easily visible and readable from a distance by approaching drivers.
- Regulations: The Australian Standard AS 1742 Manual of Uniform Traffic Control Devices is adopted by state governments, like Queensland, with amendments to specify the design, use, and placement of regulatory signs and pavement marking, including stop signs in Australia.
Stop Signs in Mexico

- Shape and Color: The stop sign in Mexico follows the international standard, which is a red octagon shape with a white border.
- Wording: The text on Mexican stop signs is white and reads “ALTO,” which, although generally means high or loud, has a secondary meaning, “stop,” and is derived from the German word Halten according to the Spanish Royal Dictionary. The text is written in bold capital letters to enhance readability and immediate recognition.
- Size: Stop signs in Mexico are required to be 30cm on each side of the octagon and include a 3 cm border.
- Regulations: In Mexico, the regulation of stop signs and other traffic signs is overseen by the Secretaría de Comunicaciones y Transportes (SCT), which translates to the Ministry of Communications and Transportation. This federal agency is responsible for maintaining and implementing transportation policies and standards, including road safety and signage.

Legal Implications of Stop Signs
Stop signs play a crucial role in regulating traffic and ensuring safety on the roads. Their importance is underscored by the legal implications and penalties associated with their non-compliance.
Understanding the role of stop signs in traffic law enforcement and the consequences of failing to adhere to them is essential for all road users.

Role of Stop Signs in Traffic Law Enforcement
- Regulating Traffic Flow: Stop signs are installed at intersections and other critical points on the road to regulate traffic flow. They ensure that vehicles stop completely before proceeding, thereby preventing accidents and improving safety.
- Determining Right-of-Way: They help in assigning the right of way. Vehicles arriving first at a stop sign have the priority to move first. This simple rule helps in avoiding confusion and potential collisions.
- Legal Enforceability: Stop signs are backed by traffic laws that vary by jurisdiction but generally follow similar principles. These laws require drivers to make a complete stop at designated points and detail what happens when drivers don’t stop when required (i.e., make a rolling stop).
- Law Enforcement Agencies: Authorities that enforce traffic laws, such as the police, ensure compliance with stop sign regulations. They monitor intersections and other critical points on the road, in person, or through automated traffic camera systems, allowing them to issue tickets for stop sign driving violations.
Penalties for Driver Non-Compliance with STOP Signs in the United States

- Fines: A monetary fine is one of the most common penalties for tickets issued by law enforcement for failing to stop at a stop sign. The amount varies by location but can be substantial, especially for repeat offenders or if the violation results in an accident.
- Points on License: Many jurisdictions operate a points system where drivers accumulate points for violations. Failing to stop at a stop sign can result in points added to the driver’s license, which can lead to increased insurance premiums and, in severe cases, the suspension of the license.
- Increased Insurance Premiums: Insurance companies often increase premiums for drivers with traffic violations, including failing to stop at stop signs. This is because such drivers are considered higher risk.
- Suspension or Revocation of License: In severe circumstances or repeated violations, a driver’s license may be suspended or revoked as it could for a DUI charge. This significant penalty underscores the seriousness with which jurisdictions treat compliance with stop sign laws.
- Criminal Charges: In some cases, particularly where non-compliance with a stop sign results in an accident causing injury or death, grossly negligent drivers may face criminal driving charges. These can include charges of reckless driving, vehicular manslaughter, or DWI offenses, depending on the jurisdiction and the specifics of the incident.
In Summary About the Purpose of Stop Signs
Stop signs are a fundamental component of traffic law enforcement, playing a vital role in regulating traffic flow and ensuring road safety.
The legal implications of failing to comply with stop sign laws underscore their importance.
Penalties for non-compliance of a regulatory sign can range from fines and points on one’s license to more severe consequences like license suspension and criminal charges.

It is imperative for all drivers to understand and adhere to stop sign regulations to ensure their safety and that of others on the road.
While the basic design of stop signs is relatively consistent worldwide—an octagonal shape with a red background and white lettering—the specific words used can vary to accommodate local languages.
Last but not least, Learn About Us.
We want to take a moment to express our gratitude for your readership and formally introduce ourselves.
We are Express Legal Funding, a nationally recognized and trusted pre-settlement funding company and brand located in Plano, Texas (the ninth largest city in Texas).

Author and Strategy Director Aaron Winston researched stop signs out in the field to write this article.
Legal Funding for Stop Sign Car Accidents
In addition to crafting expertly written and visually rich guides like this one, our core service is to provide non-recourse advances to injured and damaged plaintiffs (often involving rear-end collisions at intersections) who can’t afford to wait for their cases to settle, as they need money now.
If you find yourself in a similar predicament with your current legal claim”>claim and have already hired an attorney, we invite you to call us or apply online at any time (24/7, day or night) to learn more about how our pre-settlement funding solutions can be an excellent choice for you.


